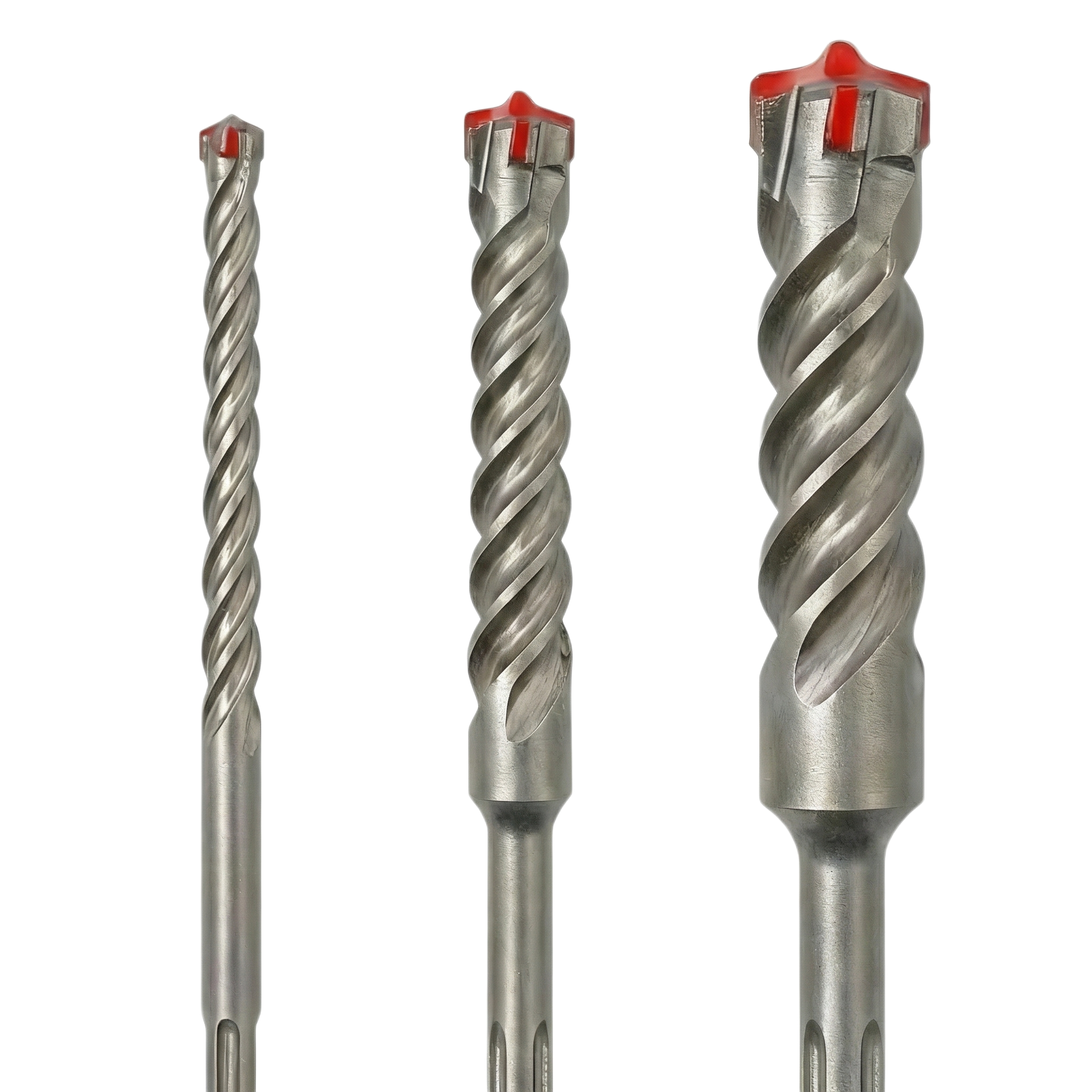
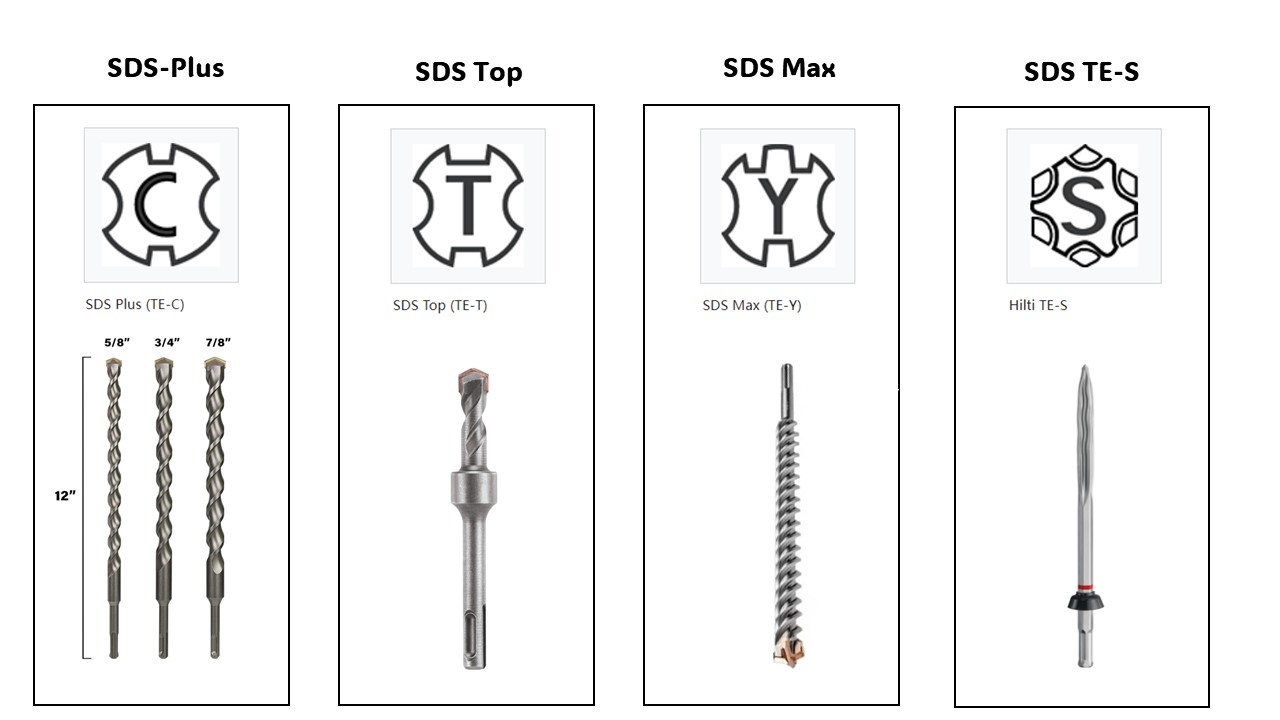
Structural Differences
The SDS (Special Direct System) revolutionized power tool connections. Unlike traditional keyed chucks, SDS uses precision grooves and steel ball locking for instant tool changes and near‑zero impact energy loss.
SDS‑Plus System Deep Dive
- Shank Diameter: 10mm standard, fits compact to mid‑size rotary hammers
- Groove Pattern: 2 open grooves (torque) + 2 closed grooves (positioning)
- Insertion Depth: 40mm for secure engagement
- Locking Mechanism: Auto‑locking steel balls, one‑hand operation
- Impact Transfer: Direct energy transfer, 95%+ efficiency
- Power Range: 500W‑1200W hammers, light to medium duty
SDS‑Max System Deep Dive
- Shank Diameter: 18mm heavy‑duty, handles extreme impact
- Groove Pattern: 3 grooves (2 open + 1 closed), optimized torque distribution
- Insertion Depth: 90mm for maximum connection strength
- Impact Capacity: Handles 15‑25 joule impact energy
- Power Range: 1200W‑2000W+ heavy‑duty hammers
- Applications: Industrial demo, large‑diameter drilling, continuous heavy duty
Hex Shank System
- Common Sizes: 17mm, 19mm, 22mm, 28mm hex
- Drive Principle: Direct torque via hex flats, superior anti‑slip
- Retention: Spring clips or threaded locks
- Advantages: High torque efficiency, ideal for high‑torque chiseling
- Typical Use: Demo chisels, breakers, large percussion tools
Detailed Application Scenarios
SDS‑Plus Applications
- Residential: Wall anchors, conduit runs, light framing
- Commercial Fit‑Out: Ceiling grid, pipe brackets, equipment mounting
- Service & Repair: HVAC install, plumbing access, equipment replacement
- Precision Work: Chemical anchors, tight tolerance holes, small‑diameter deep drilling
- Mobile Operations: Elevated work, confined spaces, frequent moves
SDS‑Max Applications
- Structural: Beam/column penetrations, heavy anchor installation
- Infrastructure: Bridge retrofits, tunnel work, foundation prep
- Industrial: Plant modifications, equipment foundations, pipe penetrations
- Demolition: Concrete breaking, structural removal, roadway repair
- Production Drilling: Batch operations, extended duty, hard materials
Hex Applications
- Demolition: Wall removal, floor breaking, tile stripping
- Surface Prep: Coating removal, rust treatment, surface leveling
- Channeling: Utility chases, drainage channels, cable runs
- Precision Chiseling: Stone carving, artistic work, restoration
Selection Strategy & Best Practices
Project Scale Considerations
- Small Projects (≤100 holes): SDS‑Plus sufficient, best cost‑effectiveness
- Medium Projects (100‑500 holes): SDS‑Plus primary, limited SDS‑Max backup
- Large Projects (500+ holes): SDS‑Max workhorse, SDS‑Plus for precision
- Demo Projects: Hex chisels + SDS‑Max drilling combination
Material Strength Matching
- C20‑C30 Concrete: SDS‑Plus standard series
- C40‑C50 High‑Strength: SDS‑Plus professional or SDS‑Max
- C60+ Ultra‑High‑Strength: SDS‑Max heavy‑duty required
- Dense Rebar Areas: SDS‑Max + cross‑head geometry preferred
ROI Analysis
- Equipment Investment: SDS‑Plus hammers moderate cost, SDS‑Max higher but greater productivity
- Consumable Costs: SDS‑Plus bits cheaper, SDS‑Max higher unit cost but potentially lower per‑hole cost
- Labor Efficiency: SDS‑Max dramatically improves large‑diameter productivity
- Maintenance: Proper selection reduces wear, extends equipment life
Safety & Operational Guidelines
- Never Cross‑Use: Forcing wrong shank types damages equipment
- Regular Inspection: Check groove wear, ball spring tension, lock reliability
- Proper Storage: Prevent groove damage, keep clean and dry
- Operator Training: Ensure familiarity with each system's characteristics